Depression is a common mental health condition that affects many people. It can make you feel sad and tired and affect your thoughts. But did you know that there are different ways to treat depression? One way is through brain stimulation therapies. These are special treatments that use magnetic fields or electricity to help the brain work better.
One of these treatments is called Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation or TMS therapy. Let’s learn more about it and how it compares to other brain stimulation therapies.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Therapy
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), or repetitive TMS, is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique that utilizes a magnetic coil to generate rapidly changing magnetic fields. When applied to specific regions of the brain, the magnetic field induces magnetic pulses, modulating neural activity in targeted areas.
TMS is primarily used to treat depression, especially for individuals who have not responded well to traditional therapies like antidepressant medications or psychotherapy. The procedure is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, offering a promising alternative for patients seeking effective relief from depression symptoms without the risks associated with invasive procedures.
While TMS therapy can be used for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), it is also being explored as a potential treatment for various mental health disorders, such as anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and certain types of chronic pain.
The Benefits of TMS Therapy
Effectiveness in treating depression
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy emerges as a promising frontier in the battle against depression. Its capacity to effectively alleviate depressive symptoms is notable. TMS can precisely stimulate nerve cells, resulting in a discernible enhancement in mood. Particularly for individuals who have found conventional remedies insufficient, TMS offers renewed hope in the journey toward recovery.
Safety and tolerability
TMS therapy is known for its exceptional safety profile, as it avoids surgical risks and doesn’t require anesthesia. It’s comfortably tolerated by most patients, involving a painless procedure with only slight tapping sensations on the scalp. Systemic side effects are reduced since it predominantly influences specific brain regions and cells. Patients can swiftly resume their usual activities, appreciating the non-disruptive nature of the treatment.
Potential side effects and their management
Although generally well-tolerated, some patients might experience mild side effects. Scalp discomfort or headaches are manageable with over-the-counter pain relief. Lightheadedness or fainting are rare, but careful monitoring during and after sessions minimizes risks. Stringent safety protocols help prevent seizures, and patients are equipped with ear protection to mitigate sound-related concerns.
Studies and Testimonials Supporting the Effectiveness of TMS Therapy
According to a review article, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) can serve as a supplementary component to psychotherapy for individuals with treatment-resistant depression, offering a favorable likelihood of achieving remission. The study reported response and remission rates of 66% and 56%, respectively, at the conclusion of the combined talk therapy and TMS treatment.
Findings from Harvard Publishing indicate that nearly 50% to 60% of individuals with major depression, who previously did not respond to medication, achieved remission with TMS therapy. Additionally, approximately one-third of these patients attain full remission, indicating the complete disappearance of their depression symptoms.
Comparisons of TMS with Other Therapies
TMS versus Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure that induces controlled seizures through electrical currents, mainly used for severe mental health conditions. It’s administered under anesthesia when other treatments are ineffective or a rapid response is necessary.
Comparison of Procedure: TMS and ECT
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is non-invasive, using magnetic fields to stimulate regions of the brain involved in mood regulation, while ECT involves controlled electric shocks under anesthesia, often leading to memory loss and confusion post-treatment. TMS is outpatient, and ECT is inpatient.
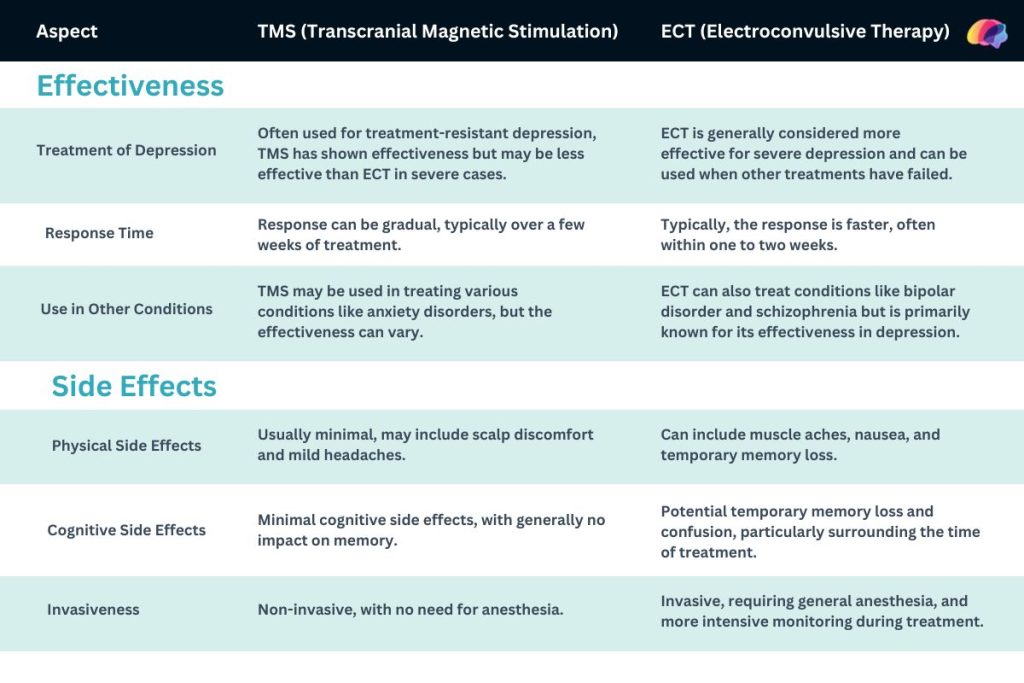
Effectiveness and Side Effects: TMS and ECT
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) are both treatments used in psychiatry, especially in managing depression. Here’s a comparison table that highlights some key differences and similarities concerning their effectiveness and side effects:
Cost Comparison: TMS and ECT
The cost comparison between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) can vary depending on factors such as location, number of sessions, and insurance coverage. On average, a full course of TMS treatment, involving around 20-30 sessions, can range from $4,000 to $12,000.
For ECT, a full course of 6-12 sessions might cost between $4,800 and $18,000 or more. However, these are rough estimates and actual costs can differ significantly based on individual circumstances and medical facilities. It’s important to consult with healthcare providers and insurance companies for more precise cost information.
TMS versus Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes into specific brain areas, delivering mild electrical impulses. It manages neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease and essential tremors.
Comparison of Procedure: TMS and DBS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes electromagnetic fields to stimulate targeted brain regions externally, while DBS requires surgical electrode implantation. TMS is a noninvasive form of therapy, while DBS involves a surgical procedure.
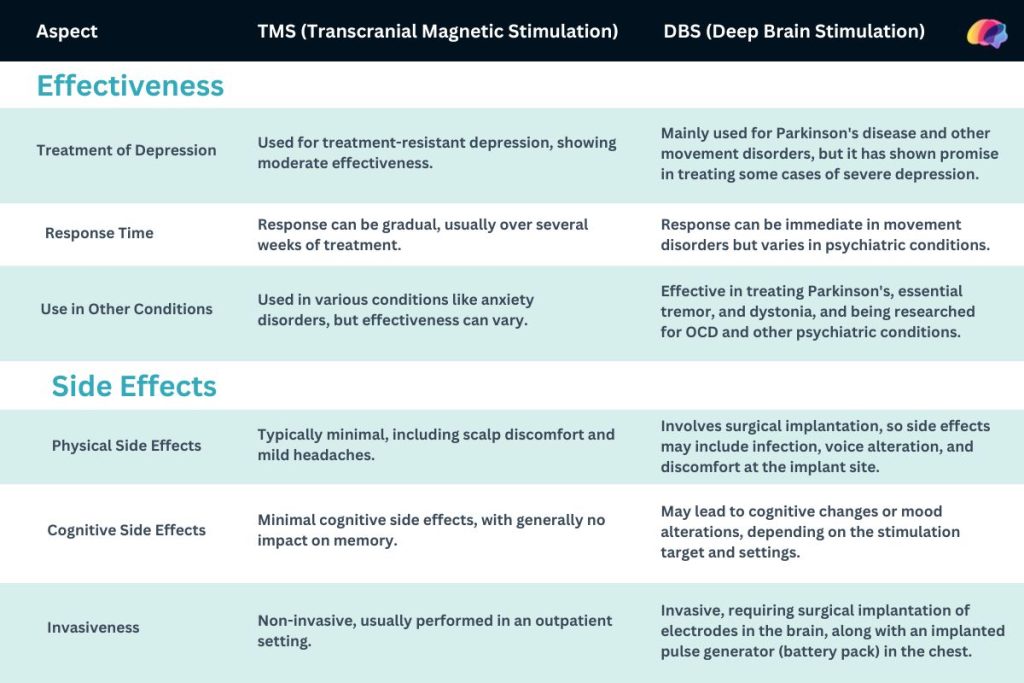
Effectiveness and Side Effects: TMS and DBS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) are both used in treating neurological and psychiatric conditions, but they differ significantly in their methods and applications. Below is a comparison table highlighting their effectiveness and side effects:
Cost Comparison: TMS and DBS
The cost comparison between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) can vary due to factors like location, medical facility, and individual needs. On average, a full course of TMS treatment, involving around 20-30 sessions, might cost between $4,000 and $12,000.
In contrast, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgery costs can range from $50,000 to $100,000 or more, including surgery, hardware implantation, and post-operative care. It’s essential to note that these estimates are approximate and can differ substantially based on specific circumstances and the medical provider.
TMS versus Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) involves implanting a device that sends electrical signals to the vagus nerve, which is used for treating epilepsy and depression.
Comparison of Procedure: TMS and VNS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) applies electromagnetic pulses externally to stimulate specific brain areas, while VNS requires surgical implantation. TMS is non-invasive, while VNS involves an implant.
Effectiveness and Side Effects: TMS and VNS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) are treatments used for various neurological and psychiatric conditions, including depression. Below is a comparison table that highlights their effectiveness and side effects:

Cost Comparison: TMS and VNS
The cost comparison between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) can vary based on factors like location, treatment duration, and individual needs. On average, a full course of TMS treatment with around 20-30 sessions may cost between $4,000 and $12,000.
In contrast, Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) implantation costs can range from $20,000 to $30,000, which includes the surgical procedure, the device, and subsequent follow-up care. However, these figures are approximate and can significantly differ based on personal circumstances and medical providers. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals and providers for precise cost information.
TMS versus Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a treatment method that involves applying low electrical currents to the scalp to modulate brain activity, used in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Comparison of Procedure: TMS and tDCS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) employs magnetic fields externally to target brain areas, while tDCS involves non-invasive electrode application on the scalp. TMS offers more localized and robust stimulation compared to tDCS.
Effectiveness and Side Effects: TMS and tDCS
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) are both non-invasive neuromodulation techniques used in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Below is a comparison table that highlights their effectiveness and side effects:

Cost Comparison: TMS and tDCS
The cost comparison between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) can vary due to factors such as location, treatment duration, and individual requirements. On average, a full course of TMS treatment with around 20-30 sessions may cost between $4,000 and $12,000.
In contrast, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) devices for home use can range from $200 to $800, while supervised clinical sessions might cost $50 to $100 per session. However, these estimates are rough and can significantly differ based on personal circumstances and treatment settings. Consulting with healthcare professionals and providers will provide more accurate cost details.
Role of Brain Stimulation Therapies in Comprehensive Treatment Plan

The integration of brain stimulation therapies with complementary treatment modalities holds significant importance within clinical practice. While brain stimulation techniques, such as TMS or DBS, offer targeted neurological interventions, they might not comprehensively address the complex interplay of physiological, psychological, and social factors underlying certain conditions.
By synergistically incorporating standard treatments such as pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, or lifestyle adjustments, a more holistic approach is realized, addressing the multifaceted nature of patients’ health conditions. This combination allows for a personalized and optimized treatment strategy, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes and enhanced overall quality of care.
TMS Therapy at Lucid Wellness Center
Lucid Wellness Center is at the forefront of providing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy, a non-invasive treatment option that holds promise for mental health improvement. Utilizing advanced TMS technology, Lucid Wellness Center offers personalized treatment plans that target specific brain regions associated with conditions like depression and anxiety. The clinic’s experienced medical professionals oversee the therapy, ensuring safety and efficacy throughout the sessions.
Lucid Wellness Center’s commitment to comprehensive care includes considering TMS as part of a holistic treatment approach, potentially integrating it with other therapies for enhanced outcomes. As the field of TMS evolves, Lucid Wellness Center remains dedicated to offering innovative solutions for individuals seeking effective and modern methods to address mental health challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the benefits of brain stimulation therapies, such as Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), are substantial and offer a ray of hope for individuals navigating various mental health challenges, such as depression. TMS, alongside other forms of brain stimulation techniques like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS), and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), provides targeted interventions that can alleviate symptoms, enhance brain function, and improve overall well-being. These therapies underscore the progress made in the realm of mental health treatment, offering options beyond traditional approaches.
Individuals must take step to seek the right treatment that aligns with their unique needs and circumstances. Mental health is a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors, and finding the most suitable therapy requires collaboration with skilled medical professionals. Whether it’s TMS or first-line treatment like medications, seeking guidance and making informed decisions ensures a tailored and effective approach to improve symptoms. Remember, the journey to well-being is a personal one, and with the advancements in brain stimulation therapies, there is a brighter prospect for individuals to find the relief and restoration they deserve.
Experience Depression Relief Today at Lucid Wellness Center
If you or a loved one are facing the challenges of treatment-resistant depression, seeking TMS therapy services is essential. Discover renewed hope with our advanced TMS therapy services. At Lucid Wellness Center, our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to guiding you toward improved mental well-being. With our state-of-the-art technology and personalized approach, we offer a non-invasive and safe solution to alleviate depression symptoms. Take the proactive step toward a brighter future and explore the potential of TMS therapy today. Don’t let depression hold you back any longer – schedule a free consultation with us now!
Frequently Asked Questions on TMS Therapy
How Is TMS Different From Other Techniques?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) sets itself apart from other brain stimulation techniques in several critical aspects. Firstly, TMS is non-invasive, avoiding surgical procedures or electrode implantation, as seen in Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Secondly, TMS allows for precise targeting of specific brain regions, focusing on areas associated with depression, unlike Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) which induces a generalized seizure. Additionally, TMS is an outpatient procedure, permitting patients to resume daily activities immediately after sessions, which contrasts with ECT, which often requires hospitalization. Lastly, TMS exhibits a lower risk of cognitive side effects than ECT, making it an attractive choice for patients seeking effective and well-tolerated treatment options for depression and other neuropsychiatric disorders.
What Is An Alternative To TMS Therapy?
An alternative to TMS therapy for treating major depression is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). ECT involves inducing a controlled seizure through electrical currents applied to the brain. While both therapies have shown efficacy in treatment-resistant depression, ECT is more invasive, may require anesthesia, and may have more pronounced cognitive side effects. The choice between TMS and ECT depends on individual patient factors, treatment history, and preferences, with each offering unique benefits and considerations in the management of depression.
What Are The Benefits Of TMS Therapy?
TMS therapy offers several benefits in the treatment of depression. It is a non-invasive procedure, which means it does not involve surgery or require any incisions. This makes it safe and well-tolerated by most patients. TMS also allows precise targeting of specific brain regions, enabling personalized treatment based on individual needs.
Additionally, it is an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to go about their daily activities immediately after each session. TMS has shown effectiveness in treating patients who have not responded well to other treatments, with the potential for rapid symptom relief and lasting improvements.
Furthermore, it generally has fewer systemic side effects compared to some antidepressant medications. As a result, TMS therapy provides hope and a better quality of life for those struggling with major depression, leading to improved mental well-being and the possibility of long-term remission.
What Is The Difference Between TMS And Neurofeedback?
The primary difference between Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Neurofeedback lies in their respective mechanisms of action and therapeutic approaches.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique that involves the application of electromagnetic pulses to specific brain regions and is primarily used for specific psychiatric disorders like severe depression. Neurofeedback, on the other hand, is a training technique that helps individuals learn to self-regulate their neural activity and is applied in a broader range of conditions, including cognitive and emotional functions, performance enhancement, and stress management. During a neurofeedback session, the person is connected to sensors that monitor brainwave patterns, and the data is displayed visually or audibly. The individual then receives feedback on their neural activity and learns to regulate and optimize their brainwave patterns through self-regulation techniques.
TMS is primarily used as a clinical application for specific psychiatric conditions, whereas Neurofeedback is utilized for a broader range of applications, including cognitive performance enhancement and stress management.
Who Should Avoid TMS Treatment?
TMS treatment may not be suitable for certain individuals, and it is essential to consider potential contraindications before undergoing the procedure. Those who should avoid TMS treatment include:
People with Metallic Implants: TMS involves the use of electromagnetic fields, which can interact with metallic implants or devices in the body. Individuals with non-removable or non-MRI compatible metal objects in or near the head, such as cochlear implants, deep brain stimulators, or aneurysm clips, may not be eligible for TMS.
History of Seizures or Epilepsy: TMS can induce electrical activity in the brain, and individuals with a history of seizures or epilepsy may be at increased risk of experiencing seizures during or after TMS therapy.
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: The safety of TMS during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been definitively established, so it is generally avoided during these periods to ensure the well-being of the mother and baby.
Active Substance Use Disorders: Individuals with active substance use disorders, especially with a history of drug or alcohol dependence, should be carefully evaluated before considering TMS treatment, as it may interfere with their recovery process.
History of Brain Injury or Neurological Disorders: Individuals with a history of significant brain injury, neurological disorders, or certain psychiatric conditions may require careful assessment and consideration before undergoing TMS.
Certain Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as uncontrolled hypertension or severe cardiovascular problems, may warrant caution or preclude TMS treatment due to potential risks.
Certain Medications: The concurrent use of certain medications, particularly those that lower seizure threshold or affect brain activity, may be incompatible with TMS treatment.
Patients should undergo a comprehensive evaluation and medical history review before considering TMS treatment to determine its suitability for their specific circumstances. It is important to discuss any medical conditions, medications, or concerns with the healthcare provider administering TMS to ensure safe and appropriate treatment decisions.

